Faster and easier than a slide rule, today we have python. :-) I wrote microflect.py, that implements some calculations from the Microflect guide and generates normalized antenna pattern plots. It will prompt for values as seen in the guide or type microflect.py --help to get a brief usage message for command line args. For completeness, microflect.bas is unchanged from the guide (possible OCR artifacts remain) and microflectConvert.py is a direct python version.
For example, running the program this way:
microflect.py -f 6.725 -a 110 -h 30 -v 40 -c v
is the same as interactively:
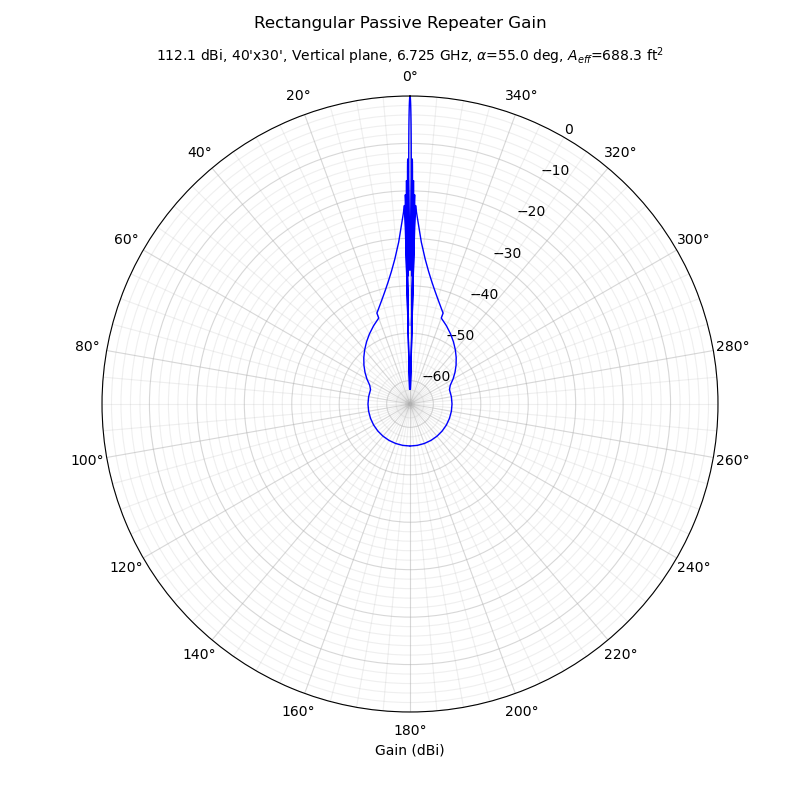
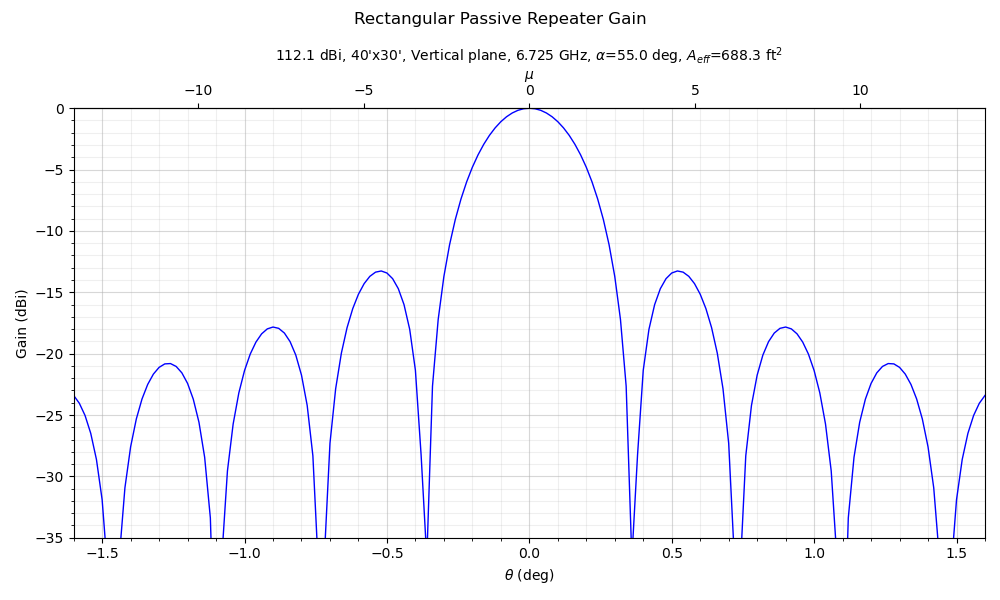
$ microflect.py Frequency in GHz: 6.725 Passive vertical length in feet: 40 Passive horizontal length in feet: 30 'H'orizontal or 'V'ertical cut: v Vertical included angle (deg) 110 Near/far field transition (Microflect): 2.84 miles Near/far field transition (Collins): 1.78 miles Effective aperture: 688.3 sq. ft. Gain: 112.1 dBi
Both pop up polar and Cartesian antenna pattern plots: