Disease Management

Featuring corn, soybeans, small grains and cucurbits: Delaware's commercial field crops are an important local industry.
Cucurbits

Factsheets
Coming soon...
All Commercial Plant Disease Fact Sheets
All Results
-
SOYBEAN VEIN NECROSIS VIRUS
Soybean Vein Necrosis Virus is an Orthotospovirus. This virus can be seed borne or vectored by multiple thrips species.
-
TAR SPOT OF CORN
Tar spot is caused by the fungal pathogen Phyllachoramaydis. Under favorable conditions for disease, yield loss on susceptible hybrids can be severe.
-
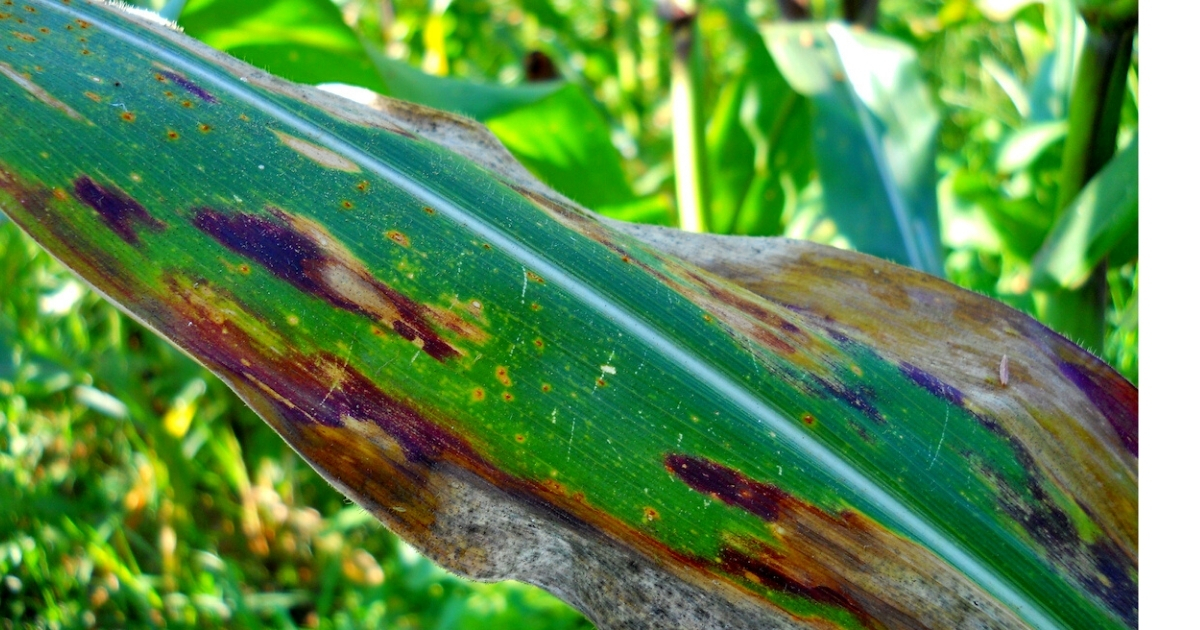
ANTHRACNOSE LEAF BLIGHT AND STALK ROT OF CORN
Anthracnose leaf blight and stalk rot of corn, caused by the fungus Colletotrichum graminicola, is a disease of worldwide importance. Yield losses can approach 40% and up to 80% lodging has been observed in fields with severe levels of anthracnose. Anthracnose can be found in corn produced in Delaware and can pose problems to local growers.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- >>
Additional Resources

Extension Experts
Weekly Crop Update
Contact
Learn more

Pest Management

Crop Production

Irrigation

Variety Trials