Corn
Corn

Sampling Guidelines
| Growth Stage: Pre-Planting | |
| Pest | Sampling Method |
| White grub, Wireworm | Sample one square foot of soil 12 inches deep; one sample should be taken for each 10 acres with a minimum of 5 sites per field; field should not be tilled before samples are taken and soil temperature at 6 inches should be 45-50 degrees F. |
| Growth Stage: Emergence to Early Whorl | |
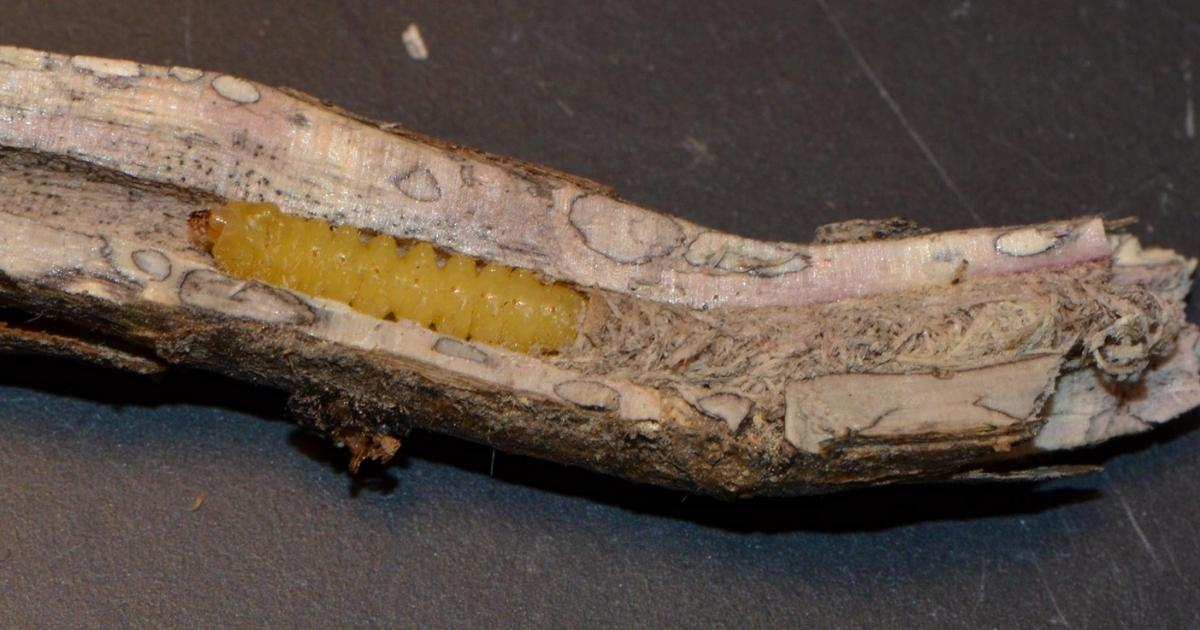
| Cutworms | Examine 10 plants in 10 locations for the presence of leaf feeding (small irregular holes) and cut plants; also look for live cutworms and estimate the average size of the larvae |
| Slugs | Examine 10 plants in 10 locations for the presence of feeding damage and slime trails; you will need to observe plants at night or during cloudy conditions to actually observe slugs feeding in plants; be sure to also check for slugs under surface trash and in open seed slots |
| Flea beetles, Cereal leaf beetle, and European corn borer | Examine 10 plants in 10 locations, count the number of beetles per plant and percent plants infested for the two beetles; count the percent infested plants for European corn borer, pull the whorls our of 5-10 plants per field to determine the size of ECB larvae as well as the average number per plant |
| Growth Stage: Mid-Whorl – Tassel Emergence | |
| Stalk borer, True Armyworm, European corn borer, Corn Earworm, Fall Armyworm | Examine 10 plants in 10 locations and count the percent infested plants |
| Growth Stage: Silking | |
| Corn rootworms | Count the number of beetles on 5 plants in 10 locations |
Insect Thresholds
Growth Stage |
|||
| Pest | Preplant | Emergence to 4 leaf stage | 5 leaf stage to silking |
| White Grubs | 1 per sq. ft. | ||
| Wireworms | 1 per sq. ft. | ||
| Slugs | 3 per sq. ft. | 3-5 per plant | |
| Cutworms | 1-2 leaf – 3% cut or 10% feeding damage 2-4 leaf – 5% cut and larvae present | ||
| Corn flea beetle | 5-6 per plant and 50% plants damaged | ||
| Common stalk borer | 2 leaf – 4% infested plants 3 leaf – 6% infested plants 4 leaf – 10% infested plants |
||
| European corn borer | 50% plants infested (irrigated)80% plants infested (non-irrigated) | 50% plants infested (irrigated)80% plants infested (non-irrigated) | |
| True armyworm | 25% plants infested and larvae < 1″ | 25% plants infested and larvae < 1″ | |
| Cereal leaf beetle | 10 per plant and 50% plants damaged | ||
| Fall armyworm | 75% plants infested with 1 worm or 50% plants with 2 or more worms | ||
| Northern corn rootworm * | 2 adult beetles per plant | ||
| Western corn rootworm * | 1 adult beetle per plant | ||
* if both present – divide number of northern corn rootworms by two and add to number of western corn rootworms
Pest Management
Recommendations for pest management
Variety trials
2023 Data
2022 Data
2021 Data
2020 Data
2019 Data
2018 Data
2017 Data
2016 Data
Field Crop Fact Sheets
All Results
-
SOYBEAN VEIN NECROSIS VIRUS
Soybean Vein Necrosis Virus is an Orthotospovirus. This virus can be seed borne or vectored by multiple thrips species.
-
TAR SPOT OF CORN
Tar spot is caused by the fungal pathogen Phyllachoramaydis. Under favorable conditions for disease, yield loss on susceptible hybrids can be severe.
-
ANTHRACNOSE LEAF BLIGHT AND STALK ROT OF CORN
Anthracnose leaf blight and stalk rot of corn, caused by the fungus Colletotrichum graminicola, is a disease of worldwide importance. Yield losses can approach 40% and up to 80% lodging has been observed in fields with severe levels of anthracnose. Anthracnose can be found in corn produced in Delaware and can pose problems to local growers.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- >>